Our guidance and advice to help manage common infections and tackle antimicrobial resistance.
We've been asked by the Department of Health and Social Care to develop evidence-based, clinical syndrome specific guidance and advice to help slow the development of antimicrobial resistances.
Existing Public Health England guidance on management and treatment of common infections will be replaced over the next few years by new NICE/PHE antimicrobial prescribing guidelines.
Guidance
Our guidelines offer evidence-based antimicrobial prescribing information for all care settings.
They focus on bacterial infections and appropriate antibiotic use. Each guideline topic features a visual summary of the recommendations, a guideline and an evidence review.
The visual summary is an overview of the guideline recommendations. It includes a prescribing table to support shared antimicrobial prescribing decisions in line with a health professional’s own clinical judgement.
An example of the draft visual summary for our sinusitis guideline
Bronchiectasis (non-cystic fibrosis), acute exacerbation
Published: December 2018
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (acute exacerbation)
Published: December 2018
Urinary tract infection (catheter-associated)
Published: November 2018
Lower UTI
Published: October 2018
Pyelonephritis (acute)
Published: October 2018
Recurrent UTI
Published: October 2018
Prostatitis (acute)
Published: October 2018
Otitis media (acute)
Published: March 2018
Sore throat (acute)
Published: January 2018
Sinusitis (acute)
Published: October 2017
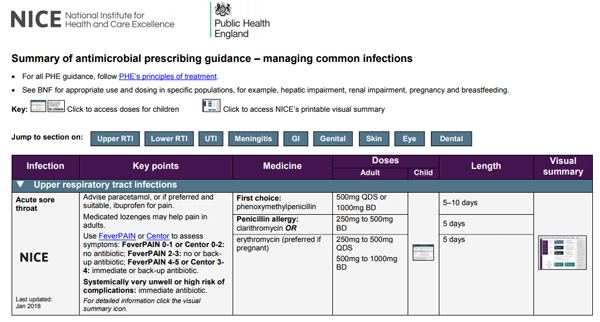
Summary of antimicrobial prescribing guidance - managing common infections
NICE and Public Health England (PHE) have brought together our information on managing common infections into a summary table. We will add a summary of new NICE guidance as it's published. We also indicate where new guidance is in development.
The evidence and rationales underpinning the information in the table can be accessed by clicking on the hyperlinks or the visual summary icons in the document.
The processes used by each organisation to develop their guidance differ. The process for developing the NICE guidelines can be found in the interim process guide. The process for developing the PHE guidance is briefly outlined on the PHE website in the PHE context, references and rationales document with further information available upon request.
This is the first time both sets of national guidance have been brought together and we would welcome your feedback. Please email infections@nice.org.uk if you have any feedback to help improve future versions.
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: In March 2019, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency issued restrictions and precautions for the use of fluoroquinolone antibiotics because of rare reports of disabling and potentially long-lasting or irreversible side effects (see Drug Safety Update for details). NICE is reviewing recommendations relating to fluoroquinolone antibiotics.
Advice
Our antimicrobial evidence summaries provide commissioners, providers and health professionals with a summary of the best available evidence for antimicrobials.
In development
We are currently developing guideline recommendations on the following topics:
Why is our guidance and advice needed?
The World Health Organization states that 'antimicrobial resistance occurs when microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites change in ways that render the medications used to cure the infections they cause ineffective'.
Resistance to antimicrobials is complex and increasing. Combined with a lack of new antimicrobial medicines, there is a growing risk that infections may not be treatable in the future.
The Department of Health and Social Care asked us to develop guidelines to help slow antimicrobial resistance. These guidelines are evidence-based and clinical syndrome specific.
Read more about the importance of antimicrobial resistance at Health matters: antimicrobial resistance.

When we as health professionals are discussing treatments for common infections with patients, it is important to talk about the benefits and harms of prescribing antibiotics. This includes the risks of antimicrobial resistance and the threat this poses to public health.Tessa Lewis, GP and Chair of the managing common infections advisory committee
How we develop guidance and advice
Antimicrobial prescribing guidelines
Find out how we develop antimicrobial prescribing guidance in the:
The scope sets out the remit for the programme:
Evidence summaries
Find out how we develop our advice in the:
Get involved
- Attend a meeting of the managing common infections advisory committee (PHAC D)
- Register as a stakeholder to take part in guidance development.
Evaluation and purchase of antimicrobials
We're beginning a project with NHS England and NHS Improvement to develop and test innovative models for the evaluation and purchase of antimicrobials.
Related guidance
Current NICE guidance and standards on antimicrobial stewardship:
Antimicrobial news at NICE

Antibiotics should not be issued as first line of treatment for a cough, says NICE and PHE
People should take honey or cough medicines instead but speak to their GP if it persists for longer than three weeks.

Double check patients with ‘penicillin allergy’ to avoid increased MRSA risk
People who incorrectly believe they are allergic to penicillin are unnecessarily put at an increased risk of developing MRSA or C difficile, NICE warns today.